# Adding Custom Code
Elevator allows administrators to add custom HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to enhance or customize the user interface. These features are only available to instance administrators.
To add a custom header, footer, or CSS to Elevator, go to: Menu > Admin > Instance Settings.
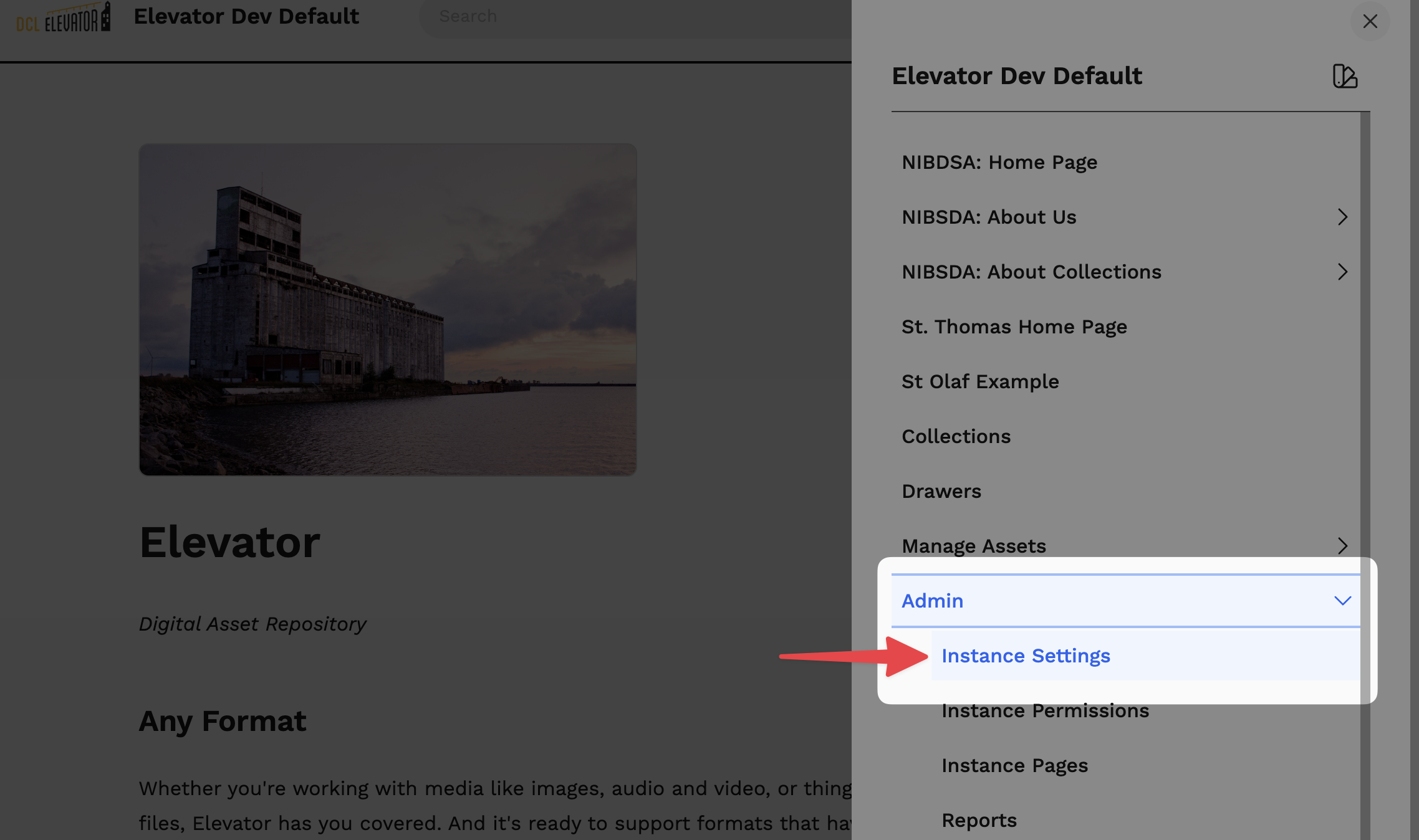
# Custom Header and Footer
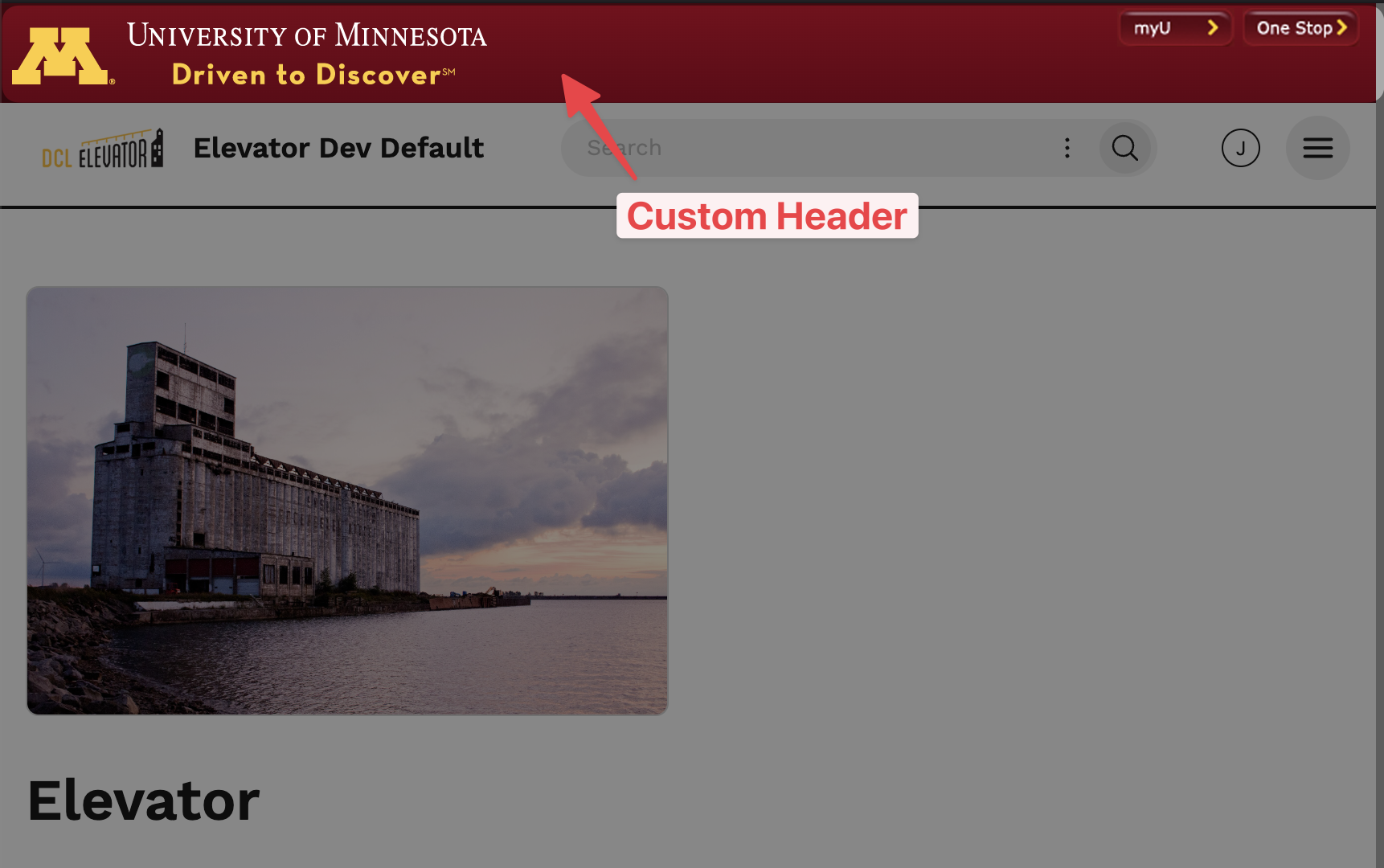
A custom header/footer is useful for adding institutional branding, banners you want your users to see, or even custom JavaScript.
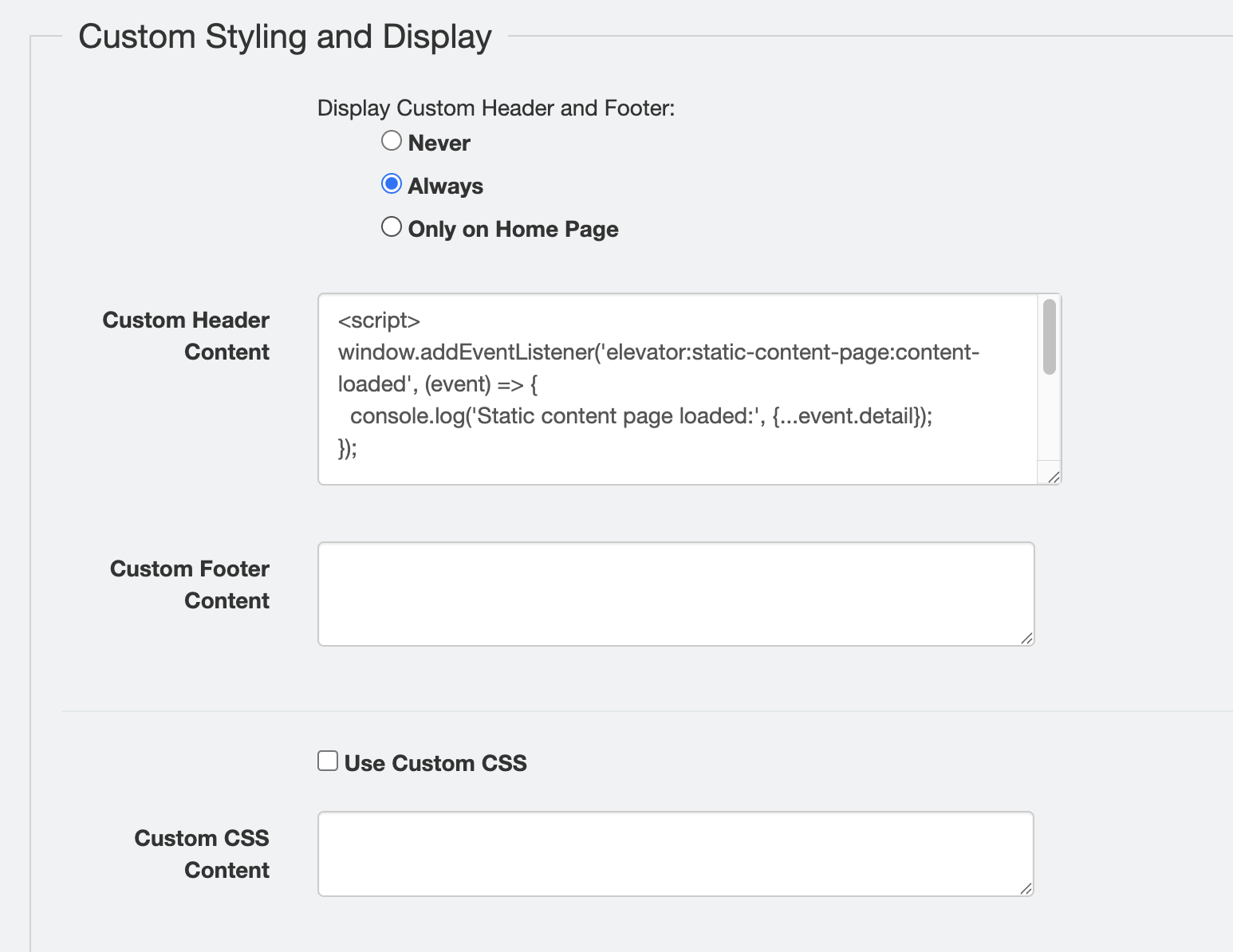
To include a custom header/footer to your Elevator instance, add the HTML, CSS, or JavaScript code in the textarea.
Display Options:
- Never (default): Custom header and footer will not appear
- Always: Custom header and footer will appear on every static page
- Only on Home Page: Custom header and footer will only appear on the home page
# Using Custom JavaScript in the Vue Interface
Elevator's Vue interface is built as a Single-Page Application (SPA), which means pages load dynamically without full page refreshes. This has important implications for custom JavaScript:
- Standard browser events like
DOMContentLoadedandwindow.loadonly fire once when the application first loads - Navigating between pages doesn't trigger these events again
To solve this, Elevator provides custom JavaScript events (opens new window) that fire whenever page content loads. These events allow your custom code to respond to navigation and content loading in the SPA environment.
# elevator:static-page:content-loaded Event
The elevator:static-page:content-loaded event fires when the page's HTML loads. Use this event when you need to interact with page content as soon as it's available.
Event Detail:
The event provides additional information in event.detail:
pageId(number): The ID of the page that was loaded
// ✅ Example
document.addEventListener('elevator:static-page:content-loaded', (event) => {
// run your custom JavaScript here
const pageId = event.detail.pageId;
console.log(`Page ${pageId} content loaded`);
});
# elevator:static-page:images-loaded Event
The elevator:static-page:images-loaded event fires when all images on the page have finished loading (or after a 10-second timeout). Use this event when you need to work with image dimensions or initialize features that depend on fully-loaded images (e.g., an image carousel).
Event Detail:
The event provides additional information in event.detail:
pageId(number): The ID of the page that was loadedimages(HTMLImageElement[]): Array of all image elements on the page
// ✅ Example
document.addEventListener('elevator:static-page:images-loaded', (event) => {
const pageId = event.detail.pageId;
const images = event.detail.images;
console.log(`Page ${pageId} has ${images.length} images loaded`);
// Initialize image-dependent features
const carousel = document.querySelector('.carousel');
if (carousel) {
initCarousel(carousel);
}
});
# Best Practices
# Use a light touch
Elevator is a dynamic platform with new features added regularly. Additionally, your users might be working on a desktop, laptop, mobile devices, or using assistive technologies like screenreaders.
Keep your custom code simple. Use standards-compliant HTML and CSS. Be wary of too much JavaScript: it could break things for some users if it's too tightly coupled to a particular interface.
# Use Event Listeners Instead of Inline Execution
❌ Don't do this:
// This only runs once when the app first loads
const carousel = document.querySelector('.carousel');
initCarousel(carousel);
✅ Do this instead:
// This runs every time a page with a carousel loads
document.addEventListener('elevator:static-page:images-loaded', (event) => {
const carousel = document.querySelector('.carousel');
if (carousel) {
initCarousel(carousel);
}
});
# Check for Element Existence
Not all pages will have the elements your code is looking for. Always check if elements exist before trying to use them, or use the pageId with the event details.
document.addEventListener('elevator:static-page:content-loaded', (event) => {
// Only create a gallery on pageId 6
if (event.detail.pageId !== 6) {
return;
}
// Check that the element exists
const gallery = document.querySelector('.photo-group');
if (!gallery) {
return; // Exit early if element doesn't exist
}
// Safe to work with gallery here
initPhotoGallery(gallery);
});
# Avoid Memory Leaks
If your code adds event listeners to page elements, make sure to clean up old handlers before adding new ones to avoid memory leaks.
let cleanupFns = [];
document.addEventListener('elevator:static-page:content-loaded', (event) => {
// Clean up old handlers
cleanupFns.forEach(cleanup => cleanup());
cleanupFns = [];
const buttons = document.querySelectorAll('.custom-button');
buttons.forEach(button => {
const handler = () => console.log('Button clicked');
button.addEventListener('click', handler);
// Create a cleanup function
const cleanup = () => button.removeEventListener('click', handler);
// Store cleanup function
cleanupFns.push(cleanup);
});
});